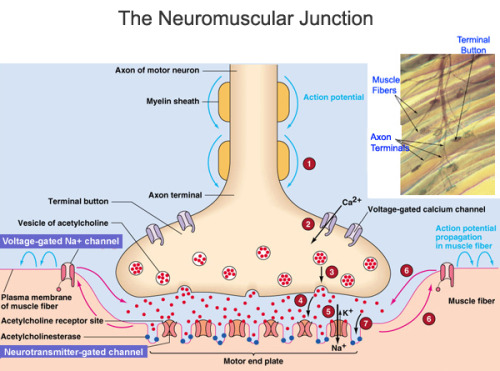
NMJ is a specialized synapse. Its job is to transmit the electrical impulses throughout the body. It does so through the motor neuron nerve terminal. Once it leaves there, these impulses are sent all over the body. There are 7 steps for sending the electrical impulse, I will quickly describe all of them for you:
Step 1: There is an electrical impulse signal that has to reach the nerve terminal in the "presynaptic" region.
Step 2: When the impulses reach the nerve terminal, they activate calcium channels.
Step 3: The increase the calcium concentration will have to trigger the fusion of the synaptic vesicles with the nerve terminal membrane.
Step 4: Once this is fused with the nerve membrane, the vesicles will release its contents into the extra cellular space, this extra space is known as the "synaptic cleft."
Step 5&6: Acetylcholine binds to its receptors. It then will open ligand-gated channels. Next an end plate potential will be created.
Step 7: The final step, Acetylcholinesterase will degrade the acetylcholine so that the process can start over again and new acetylcholine molecules can be produced.

